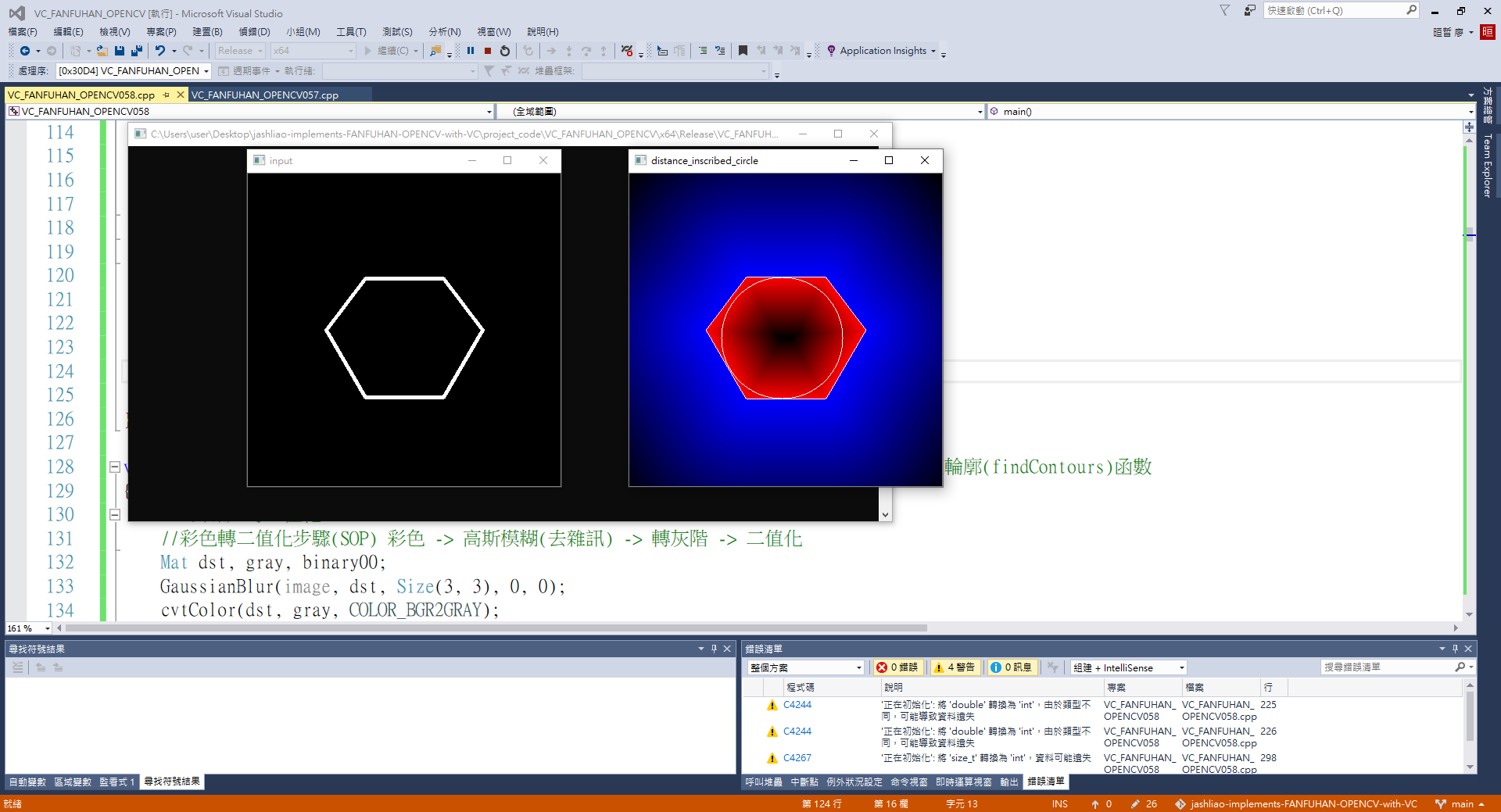
jashliao 用 VC++ 實現 fanfuhan OpenCV 教學058 ~ opencv-058-彩色轉二值化圖像(直接使用Canny) 後 連通元件(mask) 使用抓取輪廓(findContours)函數計算層次(重疊/遠近)參數,取得分類的所需資訊作業 & 對輪廓進行尋找最大內接圓(minMaxLoc)
jashliao 用 VC++ 實現 fanfuhan OpenCV 教學058 ~ opencv-058-彩色轉二值化圖像(直接使用Canny) 後 連通元件(mask) 使用抓取輪廓(findContours)函數計算層次(重疊/遠近)參數,取得分類的所需資訊作業 & 對輪廓進行尋找最大內接圓(minMaxLoc)
資料來源: https://fanfuhan.github.io/
https://fanfuhan.github.io/2019/04/18/opencv-058/
GITHUB:https://github.com/jash-git/fanfuhan_ML_OpenCV
https://github.com/jash-git/jashliao-implements-FANFUHAN-OPENCV-with-VC
★前言:

★主題:
對於輪廓來說,有時候我們會需要選擇最大內接圓,OpenCV中沒有現成的API可以使用,但是我們可以通過點多邊形測試巧妙的獲取輪廓最大內接圓的半徑,從點多邊形測試的返回結果我們知道,它返回的是像素距離,而且是當前點距離輪廓最近的距離,當這個點在輪廓內部,其返回的距離是最大值的時候,其實這個距離就是輪廓的最大內接圓的半徑,這樣我們就巧妙的獲得了圓心的位置與半徑,然後繪製。
OPENCV提供尋找最大內接圓函數(minMaxLoc)介紹如下所列:
void minMaxLoc(const Mat& src, double* minVal, double* maxVal=0, Point* minLoc=0, Point* maxLoc=0, const Mat& mask=Mat() );
void minMaxLoc(const MatND& src, double* minVal, double* maxVal, int* minIdx=0, int* maxIdx=0, const MatND& mask=MatND() );
void minMaxLoc(const SparseMat& src, double* minVal, double* maxVal, int* minIdx=0, int* maxIdx=0);
參數說明:
1 minMaxLoc尋找矩陣(一維數組當作向量,用Mat定義) 中最小值和最大值的位置.
2 參數若不需要,則置為NULL或者0,即可.
3 minMaxLoc針對Mat和MatND的重載中 ,第5個參數是可選的(optional),不使用不傳遞即可.
★C++
// VC_FANFUHAN_OPENCV058.cpp : 定義主控台應用程式的進入點。
//
/*
// Debug | x32
通用屬性
| C/C++
| | 一般
| | 其他 Include 目錄 -> ..\..\opencv411_x64\include
|
| 連結器
| |一一般
| | 其他程式庫目錄 -> ..\..\opencv411_x64\lib
|
| |一輸入
| | 其他相依性 -> opencv_world411d.lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)
// Releas | x64
組態屬性
| C/C++
| | 一般
| | 其他 Include 目錄 -> ..\..\opencv411_x64\include;%(AdditionalDependencies)
|
| 連結器
| |一般
| | 其他程式庫目錄 -> ..\..\opencv411_x64\lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)
|
| |一輸入
| | 其他相依性 -> opencv_world411.lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void blur_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum);
void edge_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum);
int getblockSum(Mat &sum, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int i);
void showHistogram(InputArray src, cv::String StrTitle);
void backProjection_demo(Mat &mat, Mat &model);
void blur3x3(Mat &src, Mat *det);
void add_salt_pepper_noise(Mat &image);
void add_gaussian_noise(Mat &image);
void USMImage(Mat src, Mat &usm, float fltPar);
void pyramid_up(Mat &image, vector<Mat> &pyramid_images, int level);
void pyramid_down(vector<Mat> &pyramid_images);
void laplaian_demo(vector<Mat> &pyramid_images, Mat &image);
void connected_component_demo(Mat &image);
void componentwithstats_demo(Mat &image);
void contours_info(Mat &image, vector<vector<Point>> &pts);
void contours_info(Mat &image, vector<vector<Point>> &pts, int threshold01, int threshold02);
void pause()
{
printf("Press Enter key to continue...");
fgetc(stdin);
}
int main()
{
const int r = 100;
Mat src = Mat::zeros(Size(4 * r, 4 * r), CV_8U);
vector<Point2f> vert(6);
vert[0] = Point(3 * r / 2, static_cast<int>(1.34 * r));
vert[1] = Point(1 * r, 2 * r);
vert[2] = Point(3 * r / 2, static_cast<int>(2.866 * r));
vert[3] = Point(5 * r / 2, static_cast<int>(2.866 * r));
vert[4] = Point(3 * r, 2 * r);
vert[5] = Point(5 * r / 2, static_cast<int>(1.34 * r));
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
line(src, vert[i], vert[(i + 1) % 6], Scalar(255), 3);
}
imshow("input", src);
// 点多边形测试
vector<vector<Point> > contours;
findContours(src, contours, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
Mat raw_dist(src.size(), CV_32F);
for (int i = 0; i < src.rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < src.cols; ++j) {
raw_dist.at<float>(i, j) = (float)pointPolygonTest(contours[0],
Point2f((float)j, (float)i), true);
}
}
// 获取最大内接圆半径
double minval, maxval;
Point maxDistPt;// save circle center
/*
void minMaxLoc(const Mat& src, double* minVal, double* maxVal=0, Point* minLoc=0, Point* maxLoc=0, const Mat& mask=Mat() );
void minMaxLoc(const MatND& src, double* minVal, double* maxVal, int* minIdx=0, int* maxIdx=0, const MatND& mask=MatND() );
void minMaxLoc(const SparseMat& src, double* minVal, double* maxVal, int* minIdx=0, int* maxIdx=0);
參數說明:
1 minMaxLoc尋找矩陣(一維數組當作向量,用Mat定義) 中最小值和最大值的位置.
2 參數若不需要,則置為NULL或者0,即可.
3 minMaxLoc針對Mat和MatND的重載中 ,第5個參數是可選的(optional),不使用不傳遞即可.
*/
minMaxLoc(raw_dist, &minval, &maxval, NULL, &maxDistPt);
minval = abs(minval);
maxval = abs(maxval);
Mat drawing = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
for (int i = 0; i < src.rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < src.cols; ++j) {
if (raw_dist.at<float>(i, j) < 0) {
drawing.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[0] = (uchar)(255 - abs(raw_dist.at<float>(i, j)) * 255 / minval);
}
else if (raw_dist.at<float>(i, j) > 0) {
drawing.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = (uchar)(255 - raw_dist.at<float>(i, j) * 255 / maxval);
}
else {
drawing.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[0] = 255;
drawing.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[1] = 255;
drawing.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = 255;
}
}
}
// 绘制内接圆
circle(drawing, maxDistPt, (int)maxval, Scalar(255, 255, 255));
imshow("distance_inscribed_circle", drawing);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void contours_info(Mat &image, vector<vector<Point>> &pts)//目標物為同類型(顏色) ~ 抓取輪廓(findContours)函數
{
// 去噪声与二值化
//彩色轉二值化步驟(SOP) 彩色 -> 高斯模糊(去雜訊) -> 轉灰階 -> 二值化
Mat dst, gray, binary00;
GaussianBlur(image, dst, Size(3, 3), 0, 0);
cvtColor(dst, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
threshold(gray, binary00, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY | THRESH_OTSU);
imshow("binary00", binary00);
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy00;
Scalar color = Scalar(255, 0, 0);
/*
void findContours(InputOutputArray image,OutputArrayOfArrays contours,OutputArray hierarchy,int mode,int method,Point offset = Point() )
各個參數詳解如下:
image表示輸入圖像,必須是二值圖像,二值圖像可以threshold輸出、Canny輸出、inRange輸出、自適應閾值輸出等。
contours獲取的輪廓,每個輪廓是一系列的點集合
hierarchy輪廓的層次信息,每個輪廓有四個相關信息,分別是同層下一個、前一個、第一個子節點、父節點
mode 表示輪廓尋找時候的拓撲結搆返回
-RETR_EXTERNAL表示只返回最外層輪廓
-RETR_TREE表示返回輪廓樹結搆
method表示輪廓點集合取得是基於什么算法,常見的是基於CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE鏈式編碼方法
*/
findContours(binary00, pts, hierarchy00, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point());
}
void contours_info(Mat &image, vector<vector<Point>> &pts, int threshold01, int threshold02)//目標物非同類型(顏色) ~ 抓取輪廓(findContours)函數
{
Mat dst, gray, binary01;
//彩色轉二值化步驟(直接使用Canny)
/*
void Canny(InputArray image, OutputArray edges, double threshold1, double threshold2, int apertureSize=3, bool L2gradient=false )
image, edges:輸入和輸出的圖片。
threshold1, threshold2:用來區分 strong edge 和 weak edge,範圍都是 0 ~ 255,會在實作過程中進一步討論,通常選擇 threshold2 / threshold1 = 1/2 ~ 1/3,例如 (70, 140), (70, 210)
apertureSize:用來計算梯度的 kernel size,也就是 Sobel 的 ksize
L2gradient:選擇要用 L1 norm(絕對值平均)還是 L2 norm(平方根)當作梯度的大小。預設是用 L1 norm
*/
Canny(image, binary01, threshold01, threshold02);
// 膨胀
/*
OpenCV提供getStructuringElement()讓我們得到要進行侵蝕或膨脹的模板
Mat getStructuringElement(int shape, Size ksize, Point anchor=Point(-1,-1))
shape:模板形狀,有MORPH_RECT、MORPH_ELLIPSE、MORPH_CROSS三種可選。
ksize:模板尺寸。
*/
Mat k = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3), Point(-1, -1));
/*
OpenCV膨脹
dilate(const Mat &src, Mat &dst, Mat kernel, Point anchor=Point(-1,-1), int iterations=1)
src:輸入圖,可以多通道,深度可為CV_8U、CV_16U、CV_16S、CV_32F或CV_64F。
dst:輸出圖,和輸入圖尺寸、型態相同。
kernel:結構元素,如果kernel=Mat()則為預設的3×3矩形,越大膨脹效果越明顯。
anchor:原點位置,預設為結構元素的中央。
iterations:執行次數,預設為1次,執行越多次膨脹效果越明顯。
*/
dilate(binary01, binary01, k);
imshow("binary01", binary01);
vector<Vec4i> hierarchy01;
Scalar color = Scalar(255, 0, 0);
findContours(binary01, pts, hierarchy01, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point());
}
void componentwithstats_demo(Mat &image)//八方鍊碼:元件標記/尋找/計算(計數)/參數:中心位置、起始座標、長、寬、面積,取得分類的所需資訊作業 + 繪製各元件的外矩形
{
// extract labels
//彩色轉二值化步驟(SOP) 彩色 -> 高斯模糊(去雜訊) -> 轉灰階 -> 二值化
Mat gray, binary;
GaussianBlur(image, image, Size(3, 3), 0);
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
threshold(gray, binary, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY | THRESH_OTSU);
imshow("input_binary", binary);
showHistogram(binary, "Histogram_input_binary");
Mat labels = Mat::zeros(image.size(), CV_32S);
Mat stats, centroids;
int num_labels = connectedComponentsWithStats(binary, labels, stats, centroids, 8, 4);
cout << "total labels : " << num_labels - 1 << endl;
vector<Vec3b> colors(num_labels);
// 背景颜色
colors[0] = Vec3b(0, 0, 0);
// 目标颜色
RNG rng;
for (int i = 1; i < num_labels; ++i) {
colors[i] = Vec3b(rng.uniform(0, 256), rng.uniform(0, 256), rng.uniform(0, 256));
}
// 抽取统计信息
Mat dst = image.clone();
for (int i = 1; i < num_labels; ++i) {
// 中心位置
int cx = centroids.at<double>(i, 0);
int cy = centroids.at<double>(i, 1);
// 统计信息
int x = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_LEFT);
int y = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_TOP);
int w = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_WIDTH);
int h = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_HEIGHT);
int area = stats.at<int>(i, CC_STAT_AREA);
// 中心位置绘制
circle(dst, Point(cx, cy), 2, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
// 外接矩形
Rect rect(x, y, w, h);
rectangle(dst, rect, colors[i]);
putText(dst, format("num:%d", i), Point(x, y), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
.5, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);
printf("num : %d, rice area : %d\n", i, area);
}
imshow("result", dst);
}
void connected_component_demo(Mat &image) //八方鍊碼 元件 計數(計算) 數量 / 標色
{
// extract labels
Mat gray, binary;
//彩色轉二值化步驟(SOP) 彩色 -> 高斯模糊(去雜訊) -> 轉灰階 -> 二值化
GaussianBlur(image, image, Size(3, 3), 0);
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
threshold(gray, binary, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY | THRESH_OTSU);
imshow("input_binary", binary);
showHistogram(binary, "Histogram_input_binary");
//計算(計數) 元件(mask) 數量 和 所需元素顏色數量陣列
/*
参数介绍如下:
image:也就是输入图像,必须是二值图,即8位单通道图像。(因此输入图像必须先进行二值化处理才能被这个函数接受)
返回值:
num_labels:所有连通域的数目
labels:图像上每一像素的标记,用数字1、2、3…表示(不同的数字表示不同的连通域)
*/
Mat labels = Mat::zeros(image.size(), CV_32S);//背景也會被算一個區域
int num_labels = connectedComponents(binary, labels, 8, CV_32S);//數量
cout << "total labels : " << num_labels - 1 << endl;
vector<Vec3b> colors(num_labels);
// 背景颜色
colors[0] = Vec3b(0, 0, 0);
// 目标颜色
RNG rng;
for (int i = 1; i < num_labels; ++i) {
colors[i] = Vec3b(rng.uniform(0, 256), rng.uniform(0, 256), rng.uniform(0, 256));
}
// 给结果着色
Mat dst = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type());
for (int row = 0; row < image.rows; ++row) {
for (int col = 0; col < image.cols; ++col) {
int label = labels.at<int>(row, col);
if (label == 0) continue;
dst.at<Vec3b>(row, col) = colors[label];
}
}
imshow("result", dst);
}
void laplaian_demo(vector<Mat> &pyramid_images, Mat &image)//拉普拉斯金字塔
{
for (int i = pyramid_images.size() - 1; i > -1; --i)
{
Mat dst;
if (i - 1 < 0)
{
pyrUp(pyramid_images[i], dst, image.size());
subtract(image, dst, dst);//圖像相減
dst = dst + Scalar(127, 127, 127); //调亮度, 实际中不能这么用
imshow(format("laplaian_layer_%d", i), dst);
}
else
{
pyrUp(pyramid_images[i], dst, pyramid_images[i - 1].size());
subtract(pyramid_images[i - 1], dst, dst);//圖像相減
dst = dst + Scalar(127, 127, 127); //調亮度, 实际中不能这么用
imshow(format("laplaian_layer_%d", i), dst);
}
}
}
void pyramid_down(vector<Mat> &pyramid_images)//高斯金字塔01
{
for (int i = pyramid_images.size() - 1; i > -1; --i) {
Mat dst;
/*
pyrUp(tmp, dst, Size(tmp.cols * 2, tmp.rows * 2))
tmp: 當前影象, 初始化為原影象 src 。
dst : 目的影象(顯示影象,為輸入影象的兩倍)
Size(tmp.cols * 2, tmp.rows * 2) : 目的影象大小, 既然我們是向上取樣, pyrUp 期待一個兩倍於輸入影象(tmp)的大小。
*/
pyrUp(pyramid_images[i], dst);
imshow(format("pyramid_down_%d", i), dst);
}
}
void pyramid_up(Mat &image, vector<Mat> &pyramid_images, int level)//高斯金字塔02
{
Mat temp = image.clone();
Mat dst;
for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i)
{
/*
pyrDown( tmp, dst, Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ))
tmp: 當前影象, 初始化為原影象 src 。
dst: 目的影象( 顯示影象,為輸入影象的一半)
Size( tmp.cols/2, tmp.rows/2 ) :目的影象大小, 既然我們是向下取樣, pyrDown 期待一個一半於輸入影象( tmp)的大小。
注意輸入影象的大小(在兩個方向)必須是2的冥,否則,將會顯示錯誤。
最後,將輸入影象 tmp 更新為當前顯示影象, 這樣後續操作將作用於更新後的影象。
tmp = dst;
*/
pyrDown(temp, dst);
imshow(format("pyramid_up_%d", i), dst);
temp = dst.clone();
pyramid_images.push_back(temp);
}
}
void USMImage(Mat src, Mat &usm, float fltPar)//圖像銳化增强演算法(USM)
{
Mat blur_img;
/*
USM銳化公式表示如下:
(源圖像– w*高斯模糊)/(1-w);其中w表示權重(0.1~0.9),默認為0.6
OpenCV中的代碼實現步驟
– 高斯模糊
– 權重疊加
– 輸出結果
*/
GaussianBlur(src, blur_img, Size(0, 0), 25);
addWeighted(src, (1 + fltPar), blur_img, (fltPar*-1), 0, usm);//原圖 : 模糊圖片= 1.5 : -0.5 的比例進行混合
imshow("usm", usm);
showHistogram(usm, "Histogram_input_usm");
}
void blur_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum)
{
int w = image.cols;
int h = image.rows;
Mat result = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type());
int x2 = 0, y2 = 0;
int x1 = 0, y1 = 0;
int ksize = 5;
int radius = ksize / 2;
int ch = image.channels();
int cx = 0, cy = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < h + radius; row++) {
y2 = (row + 1)>h ? h : (row + 1);
y1 = (row - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (row - ksize);
for (int col = 0; col < w + radius; col++) {
x2 = (col + 1)>w ? w : (col + 1);
x1 = (col - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (col - ksize);
cx = (col - radius) < 0 ? 0 : col - radius;
cy = (row - radius) < 0 ? 0 : row - radius;
int num = (x2 - x1)*(y2 - y1);
for (int i = 0; i < ch; i++) {
// 积分图查找和表,计算卷积
int s = getblockSum(sum, x1, y1, x2, y2, i);
result.at<Vec3b>(cy, cx)[i] = saturate_cast<uchar>(s / num);
}
}
}
imshow("blur_demo", result);
}
/**
* 3x3 sobel 垂直边缘检测演示
*/
void edge_demo(Mat &image, Mat &sum)
{
int w = image.cols;
int h = image.rows;
Mat result = Mat::zeros(image.size(), CV_32SC3);
int x2 = 0, y2 = 0;
int x1 = 0, y1 = 0;
int ksize = 3; // 算子大小,可以修改,越大边缘效应越明显
int radius = ksize / 2;
int ch = image.channels();
int cx = 0, cy = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < h + radius; row++) {
y2 = (row + 1)>h ? h : (row + 1);
y1 = (row - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (row - ksize);
for (int col = 0; col < w + radius; col++) {
x2 = (col + 1)>w ? w : (col + 1);
x1 = (col - ksize) < 0 ? 0 : (col - ksize);
cx = (col - radius) < 0 ? 0 : col - radius;
cy = (row - radius) < 0 ? 0 : row - radius;
int num = (x2 - x1)*(y2 - y1);
for (int i = 0; i < ch; i++) {
// 积分图查找和表,计算卷积
int s1 = getblockSum(sum, x1, y1, cx, y2, i);
int s2 = getblockSum(sum, cx, y1, x2, y2, i);
result.at<Vec3i>(cy, cx)[i] = saturate_cast<int>(s2 - s1);
}
}
}
Mat dst, gray;
convertScaleAbs(result, dst);
normalize(dst, dst, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX);
cvtColor(dst, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
imshow("edge_demo", gray);
}
int getblockSum(Mat &sum, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int i) {
int tl = sum.at<Vec3i>(y1, x1)[i];
int tr = sum.at<Vec3i>(y2, x1)[i];
int bl = sum.at<Vec3i>(y1, x2)[i];
int br = sum.at<Vec3i>(y2, x2)[i];
int s = (br - bl - tr + tl);
return s;
}
void add_gaussian_noise(Mat &image)//高斯雜訊
{
Mat noise = Mat::zeros(image.size(), image.type());
// 产生高斯噪声
randn(noise, (15, 15, 15), (30, 30, 30));
Mat dst;
add(image, noise, dst);
image = dst.clone();//dst.copyTo(image);//圖像複製
//imshow("gaussian_noise", dst);
}
void add_salt_pepper_noise(Mat &image)//白雜訊
{
// 随机数产生器
RNG rng(12345);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {
int x = rng.uniform(0, image.rows);
int y = rng.uniform(0, image.cols);
if (i % 2 == 1) {
image.at<Vec3b>(y, x) = Vec3b(255, 255, 255);
}
else {
image.at<Vec3b>(y, x) = Vec3b(0, 0, 0);
}
}
//imshow("saltp_epper", image);
}
void blur3x3(Mat &src, Mat *det)
{
// 3x3 均值模糊,自定义版本实现
for (int row = 1; row < src.rows - 1; row++) {
for (int col = 1; col < src.cols - 1; col++) {
Vec3b p1 = src.at<Vec3b>(row - 1, col - 1);
Vec3b p2 = src.at<Vec3b>(row - 1, col);
Vec3b p3 = src.at<Vec3b>(row - 1, col + 1);
Vec3b p4 = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col - 1);
Vec3b p5 = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col);
Vec3b p6 = src.at<Vec3b>(row, col + 1);
Vec3b p7 = src.at<Vec3b>(row + 1, col - 1);
Vec3b p8 = src.at<Vec3b>(row + 1, col);
Vec3b p9 = src.at<Vec3b>(row + 1, col + 1);
int b = p1[0] + p2[0] + p3[0] + p4[0] + p5[0] + p6[0] + p7[0] + p8[0] + p9[0];
int g = p1[1] + p2[1] + p3[1] + p4[1] + p5[1] + p6[1] + p7[1] + p8[1] + p9[1];
int r = p1[2] + p2[2] + p3[2] + p4[2] + p5[2] + p6[2] + p7[2] + p8[2] + p9[2];
det->at<Vec3b>(row, col)[0] = saturate_cast<uchar>(b / 9);
det->at<Vec3b>(row, col)[1] = saturate_cast<uchar>(g / 9);
det->at<Vec3b>(row, col)[2] = saturate_cast<uchar>(r / 9);
}
}
}
void backProjection_demo(Mat &image, Mat &model)//反向投影
{
Mat image_hsv, model_hsv;
cvtColor(image, image_hsv, COLOR_BGR2HSV);//彩色轉HSV
cvtColor(model, model_hsv, COLOR_BGR2HSV);
// 定义直方图参数与属性
int h_bins = 32, s_bins = 32;
int histSize[] = { h_bins, s_bins };//要切分的像素強度值範圍,預設為256。每個channel皆可指定一個範圍。例如,[32,32,32] 表示RGB三個channels皆切分為32區段
float h_ranges[] = { 0, 180 }, s_ranges[] = { 0, 256 };
const float* ranges[] = { h_ranges, s_ranges };
int channels[] = { 0, 1 };
Mat roiHist;//計算ROI的直方圖
calcHist(&model_hsv, 1, channels, Mat(), roiHist, 2, histSize, ranges);
normalize(roiHist, roiHist, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, -1, Mat());
Mat roiproj, backproj;
calcBackProject(&image_hsv, 1, channels, roiHist, roiproj, ranges);//使用反向投影 產生ROI(前景)的mask
bitwise_not(roiproj, backproj);//產生背景的mask
imshow("ROIProj", roiproj);
imshow("BackProj", backproj);
}
void showHistogram(InputArray src, cv::String StrTitle)//直方圖
{
bool blnGray = false;
if (src.channels() == 1)
{
blnGray = true;
}
// 三通道/單通道 直方圖 紀錄陣列
vector<Mat> bgr_plane;
vector<Mat> gray_plane;
// 定义参数变量
const int channels[1] = { 0 };
const int bins[1] = { 256 };
float hranges[2] = { 0, 255 };
const float *ranges[1] = { hranges };
Mat b_hist, g_hist, r_hist, hist;
// 计算三通道直方图
/*
void calcHist( const Mat* images, int nimages,const int* channels, InputArray mask,OutputArray hist, int dims, const int* histSize,const float** ranges, bool uniform=true, bool accumulate=false );
1.輸入的圖像數組
2.輸入數組的個數
3.通道數
4.掩碼
5.直方圖
6.直方圖維度
7.直方圖每個維度的尺寸數組
8.每一維數組的範圍
9.直方圖是否是均勻
10.配置階段不清零
*/
if (blnGray)
{
split(src, gray_plane);
calcHist(&gray_plane[0], 1, 0, Mat(), hist, 1, bins, ranges);
}
else
{
split(src, bgr_plane);
calcHist(&bgr_plane[0], 1, 0, Mat(), b_hist, 1, bins, ranges);
calcHist(&bgr_plane[1], 1, 0, Mat(), g_hist, 1, bins, ranges);
calcHist(&bgr_plane[2], 1, 0, Mat(), r_hist, 1, bins, ranges);
}
/*
* 显示直方图
*/
int hist_w = 512;
int hist_h = 400;
int bin_w = cvRound((double)hist_w / bins[0]);
Mat histImage = Mat::zeros(hist_h, hist_w, CV_8UC3);
// 归一化直方图数据
if (blnGray)
{
normalize(hist, hist, 0, histImage.rows, NORM_MINMAX, -1);
}
else
{
normalize(b_hist, b_hist, 0, histImage.rows, NORM_MINMAX, -1);
normalize(g_hist, g_hist, 0, histImage.rows, NORM_MINMAX, -1);
normalize(r_hist, r_hist, 0, histImage.rows, NORM_MINMAX, -1);
}
// 绘制直方图曲线
for (int i = 1; i < bins[0]; ++i)
{
if (blnGray)
{
line(histImage, Point(bin_w * (i - 1), hist_h - cvRound(hist.at<float>(i - 1))),
Point(bin_w * (i), hist_h - cvRound(hist.at<float>(i))), Scalar(255, 255, 255),
2, 8, 0);
}
else
{
line(histImage, Point(bin_w * (i - 1), hist_h - cvRound(b_hist.at<float>(i - 1))),
Point(bin_w * (i), hist_h - cvRound(b_hist.at<float>(i))), Scalar(255, 0, 0),
2, 8, 0);
line(histImage, Point(bin_w * (i - 1), hist_h - cvRound(g_hist.at<float>(i - 1))),
Point(bin_w * (i), hist_h - cvRound(g_hist.at<float>(i))), Scalar(0, 255, 0),
2, 8, 0);
line(histImage, Point(bin_w * (i - 1), hist_h - cvRound(r_hist.at<float>(i - 1))),
Point(bin_w * (i), hist_h - cvRound(r_hist.at<float>(i))), Scalar(0, 0, 255),
2, 8, 0);
}
}
imshow(StrTitle, histImage);
}
★Python
from __future__ import print_function
from __future__ import division
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
# Create an image
r = 100
src = np.zeros((4*r, 4*r), dtype=np.uint8)
# Create a sequence of points to make a contour
vert = [None]*6
vert[0] = (3*r//2, int(1.34*r))
vert[1] = (1*r, 2*r)
vert[2] = (3*r//2, int(2.866*r))
vert[3] = (5*r//2, int(2.866*r))
vert[4] = (3*r, 2*r)
vert[5] = (5*r//2, int(1.34*r))
# Draw it in src
for i in range(6):
cv.line(src, vert[i], vert[(i+1)%6], ( 255 ), 3)
# Get the contours
_, contours, _ = cv.findContours(src, cv.RETR_TREE, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# Calculate the distances to the contour
raw_dist = np.empty(src.shape, dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(src.shape[0]):
for j in range(src.shape[1]):
raw_dist[i,j] = cv.pointPolygonTest(contours[0], (j,i), True)
# 获取最大值即内接圆半径,中心点坐标
minVal, maxVal, _, maxDistPt = cv.minMaxLoc(raw_dist)
minVal = abs(minVal)
maxVal = abs(maxVal)
# Depicting the distances graphically
drawing = np.zeros((src.shape[0], src.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
for i in range(src.shape[0]):
for j in range(src.shape[1]):
if raw_dist[i,j] < 0:
drawing[i,j,0] = 255 - abs(raw_dist[i,j]) * 255 / minVal
elif raw_dist[i,j] > 0:
drawing[i,j,2] = 255 - raw_dist[i,j] * 255 / maxVal
else:
drawing[i,j,0] = 255
drawing[i,j,1] = 255
drawing[i,j,2] = 255
# max inner circle
cv.circle(drawing,maxDistPt, np.int(maxVal),(255,255,255), 1, cv.LINE_8, 0)
cv.imshow('Source', src)
cv.imshow('Distance and inscribed circle', drawing)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()