一把梭系列 ~ C語言範例 (0014) [字串 的 比較、搜尋、轉換]
一把梭系列 ~ C語言範例 (0014) [字串 的 比較、搜尋、轉換]
資料來源: https://openhome.cc/Gossip/CGossip/StringCmpSearch.html
https://openhome.cc/Gossip/CGossip/StringParseTest.html
https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cwchar/wcscmp/
https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cwchar/wcsncmp/
https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cwchar/wcsstr/
https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cwchar/wcsspn/
https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cwchar/wcscspn/
https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cwchar/wcspbrk/
http://www.cppfans.com/cbknowledge/reference/cstdlib/atof.asp
http://www.cppfans.com/cbknowledge/reference/cstdlib/atoi.asp
http://www.cppfans.com/cbknowledge/reference/cstdlib/atol.asp
http://www.cppfans.com/cbknowledge/reference/cstdlib/itoa.asp
http://www.cppfans.com/cbknowledge/reference/cstdlib/ltoa.asp
https://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cwchar/fgetws/
★前言:

★主題:
在〈字元陣列與字串〉說過,在 C 語言中,字串是一個字元陣列,最後一個字元以空字元 ‘\0’ 作結尾。
但由於它就具有各元素依序組合後的實際單詞義意,並且也依照不同編碼格式而有所不同,因此C語言有提供一系列的對應函數方便使用者使用。
下面我們就將C語言提供的相關功能進行分門別類的初步整理與介紹:
01.字串比較
int strcmp(const char *lhs, const char *rhs);
int strncmp(const char *lhs, const char *rhs, size_t count);
int wcscmp (const wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2);
int wcsncmp (const wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2, size_t num);
02.字串搜尋
int strncmp ( const char * str1, const char * str2, size_t num );//比對N個字元
char *strstr(const char* str, const char* substr);//相同/重複/子字串
size_t strspn(const char *dest, const char *src);//不相同/差異
size_t strcspn( const char *dest, const char *src );//找出一個字串中與另一個字串任何字元第一次匹配的索引位置
char* strpbrk(const char* dest, const char* breakset);
int wcsncmp (const wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2, size_t num);//比對N個字元
const wchar_t* wcsstr (const wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2);//相同/重複/子字串
wchar_t* wcsstr (wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2);
size_t wcsspn (const wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2);//不相同/差異
size_t wcscspn (const wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2);//找出一個字串中與另一個字串任何字元第一次匹配的索引位置
const wchar_t* wcspbrk (const wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2);
wchar_t* wcspbrk (wchar_t* wcs1, const wchar_t* wcs2);
03.字串轉換
//字串轉數值(浮點數/整數)
double atof(const char* str);
int atoi(const char *str);
long atol(const char *str);
//數值(整數)轉字串
char *itoa(int v, char *s, int r);
char *ltoa(long v, char *s, int r);
//字串轉數值(浮點數/整數)
double _wtof(const wchar_t *s);
int _wtoi(const wchar_t *s);
long _wtol(const wchar_t *s);
//數值(整數)轉字串
wchar_t *_itow(int v, wchar_t *s, int r);
wchar_t *_ltow(long v, wchar_t *s, int r);
★code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <locale.h>
#include <string.h>
#define LEN 80
int main()
{
//*
//預設編碼環境設定:
//Setting -> Editor ->Global compiler settings->Other options -> default
//Build options->compiler settings->Other options []
//字串比對- strncmp(比對N個字元)
printf("字串比對- strncmp(比對N個字元)\n");
char passwd[] = "123456";
char buf[LEN];
printf("請輸入密碼:");
fgets(buf, LEN, stdin);// 123456 / 0123456 / 1234560
if(strncmp(passwd, buf, 6) == 0)
{
puts("密碼正確");
}
else
{
puts("密碼錯誤");
}
//字串搜尋- strstr(相同/重複/子字串)
printf("\n字串搜尋- strstr(相同/重複/子字串)\n");
char source01[LEN];
char search01[LEN];
printf("輸入字串:");
fgets(source01, LEN, stdin);// How do you do?
printf("搜尋子字串:");// you / do you / you do
fgets(search01, LEN, stdin);
search01[strlen(search01) - 1] = '\0';// 去除最後的換行字元,否則會造成函數異常
char *loc = strstr(source01, search01);
if(loc == NULL)
{
printf("找不到符合的子字串\n");
}
else
{
printf("在索引位置 %lu 處找到子字串\n", loc - source01);
}
//字串搜尋- strspn(不相同/差異)
printf("\n字串搜尋- strspn(不相同/差異)\n");
char str1[LEN];
char str2[LEN];
printf("輸入字串:");
fgets(str1, LEN, stdin);// How do you do?
printf("搜尋子字串:");
fgets(str2, LEN, stdin);// How do / How do joe do / do you do?
str2[strlen(str2) - 1] = '\0';// 去除最後的換行字元,否則會造成函數異常
size_t loc01 = strspn(str1, str2);
if(loc01 == strlen(str1))
{
printf("完全匹配\n");
}
else
{
printf("從索引位置 %lu 處開始不匹配\n", loc01);
}
//字串搜尋- strcspn(找出一個字串中與另一個字串任何字元第一次匹配的索引位置)
printf("\n字串搜尋- strcspn(找出一個字串中與另一個字串任何字元第一次匹配的索引位置)\n");
printf("輸入字串:");
fgets(str1, LEN, stdin); // How do you do?
printf("搜尋子字串:");
fgets(str2, LEN, stdin);// How do / How do joe do / do you do?
str2[strlen(str2) - 1] = '\0';// 去除最後的換行字元,否則會造成函數異常
size_t loc02 = strcspn(str1, str2);
if(loc02 == strlen(str1))
{
printf("沒有任何字元匹配\n");
}
else
{
printf("索引位置 %lu 處匹配到字元\n", loc02);
}
printf("\n字串轉數字\n");
printf("\"1010\"\t二進位:\t%ld\n", strtol("1010", NULL, 2));
printf("\"12\"\t八進位:\t%ld\n", strtol("12", NULL, 8));
printf("\"A\"\t十六進位:\t%ld\n", strtol("A", NULL, 16));
printf("\"012\"\t自動基底:\t%ld\n", strtol("012", NULL, 0));
printf("\"0xA\"\t自動基底:\t%ld\n", strtol("0xA", NULL, 0));
printf("\"junk\"\t自動基底:\t%ld\n", strtol("junk", NULL, 0));
//*/
/*
//使用寬字串/UTF-8 環境設定:
//Setting -> Editor ->Global compiler settings->Other options -> UTF-8
//Build options->compiler settings->Other options [-finput-charset=UTF-8]
setlocale(LC_ALL, "");
//字串比對- wcsncmp(比對N個字元)
wprintf(L"字串比對- wcsncmp(比對N個字元)\n");
wchar_t *passwd = L"123456";
wchar_t buf[LEN];
wprintf(L"請輸入密碼:");
fgetws(buf,LEN,stdin);// 123456 / 0123456 / 1234560
if(wcsncmp(passwd, buf, 6) == 0)
{
wprintf(L"密碼正確\n");
}
else
{
wprintf(L"密碼錯誤\n");
}
//字串搜尋- wcsstr(相同/重複/子字串)
wprintf(L"\n字串搜尋- wcsstr(相同/重複/子字串)\n");
wchar_t source01[LEN];
wchar_t search01[LEN];
wprintf(L"輸入字串:");
fgetws(source01,LEN,stdin);// How do you do?
wprintf(L"搜尋子字串:");// you / do you / you do
fgetws(search01,LEN,stdin);
search01[wcslen(search01) - 1] = '\0';// 去除最後的換行字元,否則會造成函數異常
wchar_t *loc = wcsstr(source01, search01);
if(loc == NULL)
{
wprintf(L"找不到符合的子字串\n");
}
else
{
wprintf(L"在索引位置 %lu 處找到子字串\n", loc - source01);
}
//字串搜尋- wcsspn(不相同/差異)
wprintf(L"\n字串搜尋- wcsspn(不相同/差異)\n");
wchar_t str1[LEN];
wchar_t str2[LEN];
wprintf(L"輸入字串:");
fgetws(str1,LEN,stdin);// How do you do?
wprintf(L"搜尋子字串:");
fgetws(str2,LEN,stdin);// How do / How do joe do / do you do?
str2[wcslen(str2) - 1] = '\0';// 去除最後的換行字元,否則會造成函數異常
size_t loc01 = wcsspn(str1, str2);
if(loc01 == wcslen(str1))
{
wprintf(L"完全匹配\n");
}
else
{
wprintf(L"從索引位置 %lu 處開始不匹配\n", loc01);
}
//字串搜尋- wcscspn(找出一個字串中與另一個字串任何字元第一次匹配的索引位置)
wprintf(L"\n字串搜尋- wcscspn(找出一個字串中與另一個字串任何字元第一次匹配的索引位置\n");
wprintf(L"輸入字串:");
fgetws(str1,LEN,stdin); // How do you do?
wprintf(L"搜尋子字串:");
fgetws(str2,LEN,stdin);// How do / How do joe do / do you do?
str2[wcslen(str2) - 1] = '\0';// 去除最後的換行字元,否則會造成函數異常
size_t loc02 = wcscspn(str1, str2);
if(loc02 == wcslen(str1))
{
wprintf(L"沒有任何字元匹配\n");
}
else
{
wprintf(L"索引位置 %lu 處匹配到字元\n", loc02);
}
wprintf(L"\n字串轉數字\n");
wprintf(L"\"1010\"\t二進位:\t%ld\n", strtol("1010", NULL, 2));
wprintf(L"\"12\"\t八進位:\t%ld\n", strtol("12", NULL, 8));
wprintf(L"\"A\"\t十六進位:\t%ld\n", strtol("A", NULL, 16));
wprintf(L"\"012\"\t自動基底:\t%ld\n", strtol("012", NULL, 0));
wprintf(L"\"0xA\"\t自動基底:\t%ld\n", strtol("0xA", NULL, 0));
wprintf(L"\"junk\"\t自動基底:\t%ld\n", strtol("junk", NULL, 0));
//*/
return 0;
}
★結果:
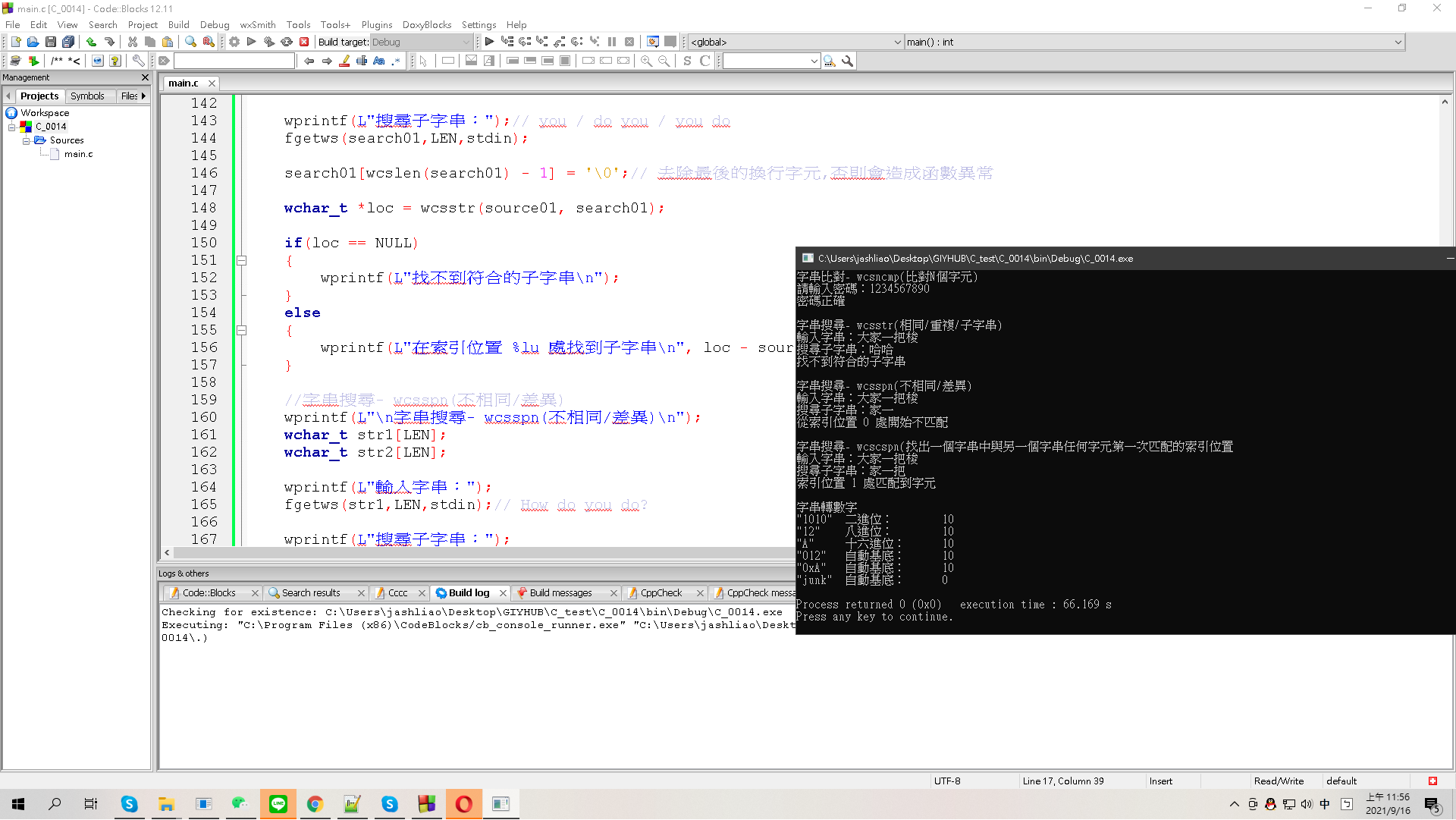
★延伸說明/重點回顧:
01.C語言的字串就是字元陣列
02.從函數介紹可以大致發現寬字串和標準字串函數用法觀念幾乎一致,其差別就只有函數名稱和參數型態
03.這些函數是為了進行『資料分析/資料清洗』和『資料組合』的前置動作,對於日後非常實用建議好好收藏
04.各種C/C++的函示庫: QT/BCB/VC++ 都有自己的類似函數,但是都和標準C語言類似,所以只要學會基礎要轉到其他的平台就很容易了
05.寬字串模式(wchar_t)支援中文字搜尋
One thought on “一把梭系列 ~ C語言範例 (0014) [字串 的 比較、搜尋、轉換]”
C/C++
若要測試字元為數字、字母、大寫、小寫等等,可以使用 ctype.h 中的 isxxxx() 函式,例如:
isalnum(int c):是否為字母或數字
isalpha(int c):是否為字母
iscntrl(int c):是否為控制字元
isdigit(int c):是否為數字
islower(int c):是否為小寫字母
isprint(int c):是否為列印字元
ispunct(int c):是否為標點符號
isspace(int c):是否為空白
isupper(int c):是否為大寫字母
isxdigit(int c):是否為16進位數字
…
這些函式事實上是巨集,可以查看 ctype.h 得知更多的 isxxxx 函式,ctype.h 中也包括了像是可以進行字母大小寫轉換的 tolower、toupper 等函式。